A recent study conducted at UKE Hamburg compared manual and software-assisted assessments of computed tomography (CT) scans according to iRECIST (immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) in oncological patients undergoing immune-based treatment. Utilizing mint Lesion™ for software-assisted assessment, the study found that software-assisted assessments resulted in shorter reading times, lower error rates, and higher inter-reader agreement compared to manual assessments. The researchers thus concluded that software-assisted iRECIST assessments are preferable over manual approaches for optimal oncological response evaluation.
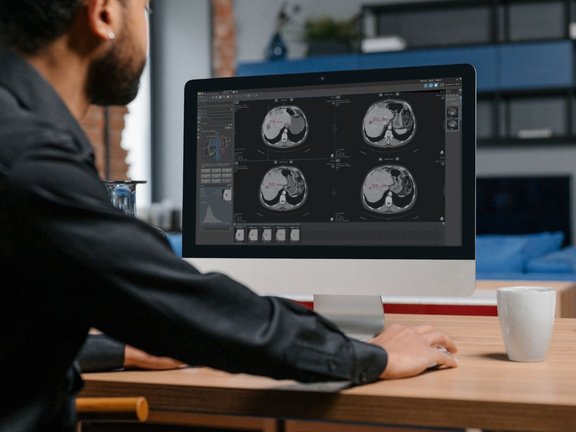

Software-Assisted CT Assessment Outperforms Manual Methods in Oncology Study
Related Resources
Related Resources

Healthcare on FHIR: Igniting the Potential of Interoperability
Interoperability plays a crucial role in healthcare: it enables seamless communication of patient information across different systems, leads to…

Optimizing Glioblastoma Imaging: Enhancing MRI Efficiency and Quality with Deep Learning
This study investigates the use of deep learning (DL) to optimize MRI protocols for glioblastoma patients, aiming to reduce scan time and improve…
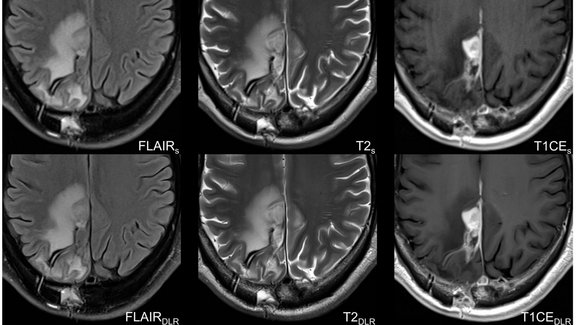
University Hospital Tübingen: Advancing MRI Efficiency in Glioblastoma Care with Deep Learning
This study explores the use of deep learning (DL) to optimize MRI protocols for glioblastoma patients. Glioblastomas, known for being the most…