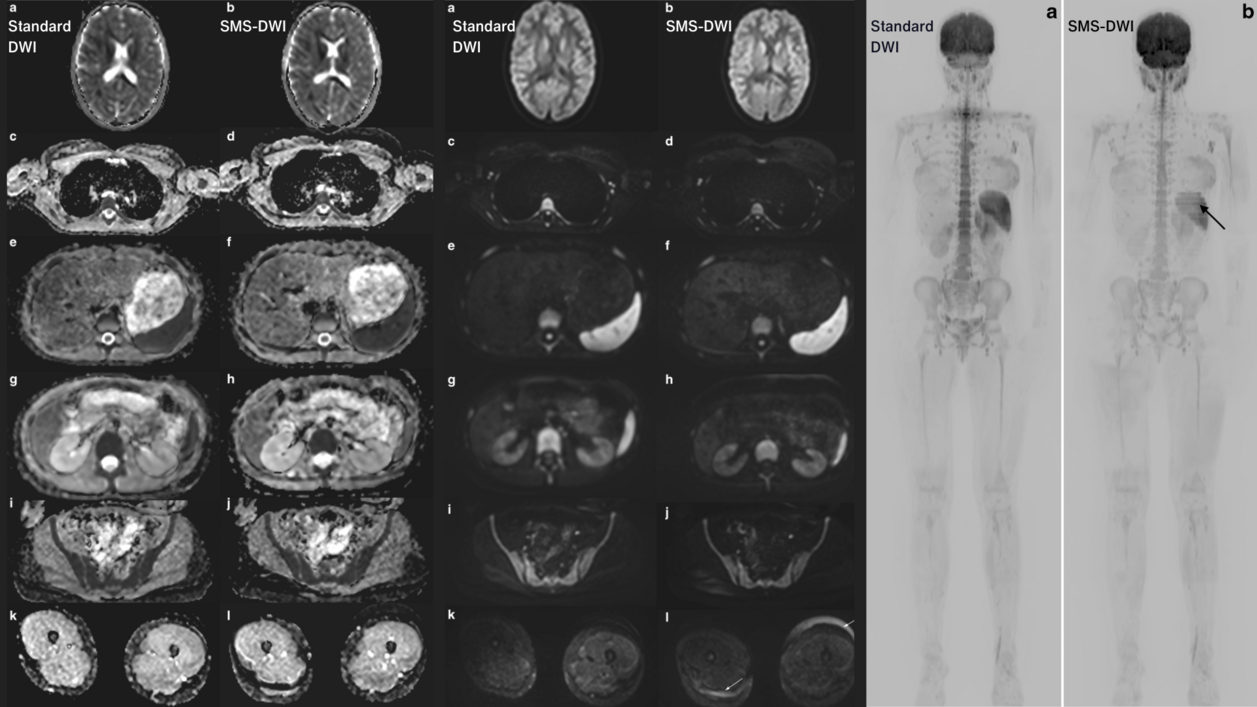
This study[1] addressed the challenges of conducting WB-MRI in paediatric patients, particularly the prolonged acquisition time required for diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), which is a crucial component of the WB-MRI protocol. DWI is important for enhancing image interpretation and sensitivity, but its longer acquisition time can be challenging, especially with younger patients who may have difficulty remaining still for extended periods.
The main objectives of the study were to compare the acquisition time, image quality, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the new interleaved STIR SMS-DWI sequence with a standard non-accelerated DWI sequence in paediatric WB-MRI. Additionally, the study aimed to determine whether the new technique could offer equivalent image quality while significantly reducing the acquisition time.
The study included 20 children and adolescents who underwent two WB-MRI scans using either the standard DWI or the SMS-DWI sequence. mint Lesion™ software was used to quantitatively assess SNR and ADC in seven different areas, including white matter, cerebrospinal fluid, mediastinum, liver, spleen, kidneys, and thigh muscles, at b = 800 s/mm2 and on the ADC parameter map. The software ensured consistent region of interest (ROI) sizes and positions across different images. For each ROI, mint Lesion™ automatically obtained mean, standard deviation, and maximum values, and calculated SNR for b800. Additionally, two experienced paediatric radiologists used the software for qualitative assessment to evaluate image quality using a 5-point Likert scale. They assessed brain, chest, trunk, and extremities for each patient, considering factors like distortion-free imaging, artifacts, and overall quality.
The researchers concluded that the interleaved STIR SMS-DWI sequence is a promising technique for paediatric WB-MRI, as it significantly reduces the time needed for the imaging procedure without compromising the quality of the images. This could be particularly beneficial for younger patients who may struggle with longer scan times and contribute to more efficient and effective clinical imaging in paediatric oncology and other medical scenarios.
Read the original publication here.
[1] Krueger, PC., Krämer, M., Benkert, T. et al. Whole-body diffusion magnetic resonance imaging with simultaneous multi-slice excitation in children and adolescents. Pediatr Radiol 2023