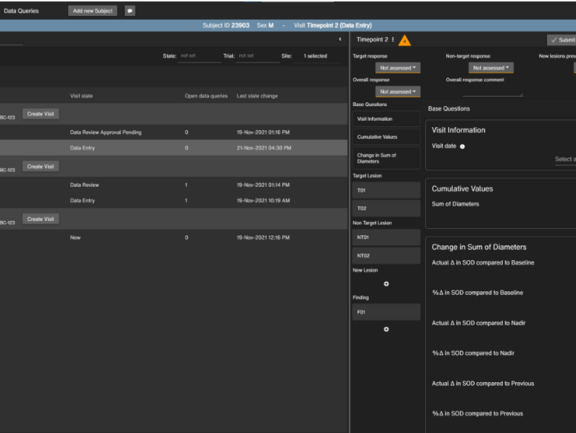
Whether in clinical routine, in clinical trials or in clinical research, mint Lesion™ is a reliable and strong supporter of its users’ individual workflows. To enhance this role further and offer even more opportunities to benefit from structured data, we are currently developing a browser-based application which can be used complimentary to the mint Lesion™ client or even independently for purposes such as electronic data capture (EDC).
The web application offers an optimized user interface for specific tasks, according to the specific user and use scenario. In clinical trials, various parties such as Principal Investigators, sponsors or contract research associates might want to take a look at and review certain collected data without having to look at the radiological images themselves. With the browser-based application, users can gain access to this data depending on their role. It can be used as a stand-alone EDC system for the collection of trial data, review and verification of data, as well as reporting. When used with mint Lesion™, it provides a direct link to the imaging and provide all of the benefits of the mint Lesion™ backend, such as conformity checks, longitudinality, pre-defined workflows, and more. For clinical routine, the browser-based application offers additional advantages, such as the opportunity to share the data with multidisciplinary tumor boards or even, to some degree, with patients.
It will be used as an EDC system in the project KoMed at the University Hospital Heidelberg, about which you can read more here. We are looking forward to this next exciting development with which interdisciplinary communication and the information flow between departments, referring colleagues and patients will improve immensely.
Structure, Gather, and Share Data Faster with the mint Lesion™ Browser-Based Application
Related Resources
Related Resources

RACOON SAGA: Interdisciplinary Research for Better Therapy Decisions in Sarcoma Treatment
Sarcomas are rare tumors that pose particular challenges to both medicine and research. Their heterogeneity makes precise diagnostics difficult, which…

The Template Designer in Use: Interview with Dr. Madelaine Hettler
Structured, well-organized data are the foundation of meaningful research. But how can they be captured effectively in practice? Dr. Madelaine…

Research Insights from Dr. Madelaine Hettler: The Template Designer in Use
Structured and well-organized data are essential building blocks for successful research and clinical projects. The Template Designer provides a tool…