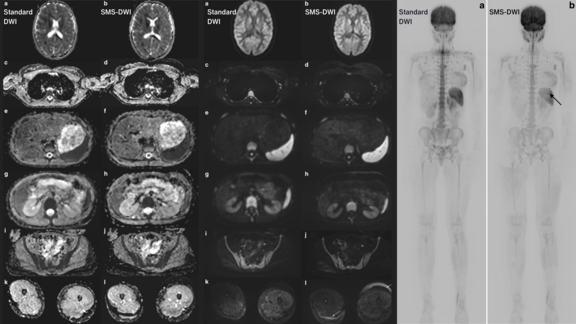
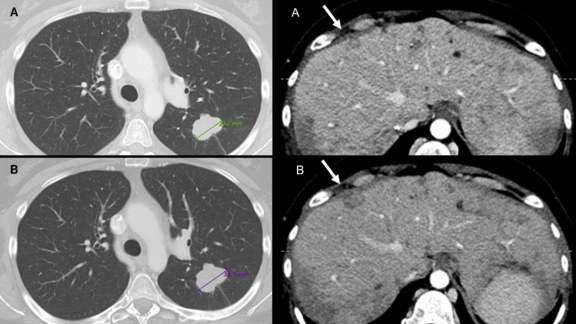
Since mid-2020, mint Lesion™ has been successfully used within the Radiological Cooperative Network (RACOON), in the University Medicine Network which unites all 38 university hospitals in Germany. RACOON was the first project of this scale to establish a nationwide infrastructure for the structured collection of radiological data from COVID-19 cases.
As an industry partner, Mint Medical provides the technological basis ("RACOON Base") for the collection and analysis of radiological data. mint Lesion™ plays a central role in the project, forming the backbone of the RACOON infrastructure and making all patient information documented on site (e.g., lab values, treatment history, etc.) available to the users via interfaces between the reporting platform and other local data sources (RIS, HIS, etc.). The reporting process delivered by mint Lesion™ fulfils all requirements for data completeness, traceability and conformity with guidelines, thereby ensuring the implementation of good scientific practice.
The project initially started as a platform for the acquisition and analysis of radiological data from COVID-19 cases, however, it soon became evident that the created infrastructure has a high scaling potential and can also be extended to numerous other areas of application. The network will therefore be expanded in the coming years (2022 - 2024), both through further development of the basic infrastructure and through the integration of new application areas, e.g., in the fields of neurological, cardiological, and pediatric imaging.