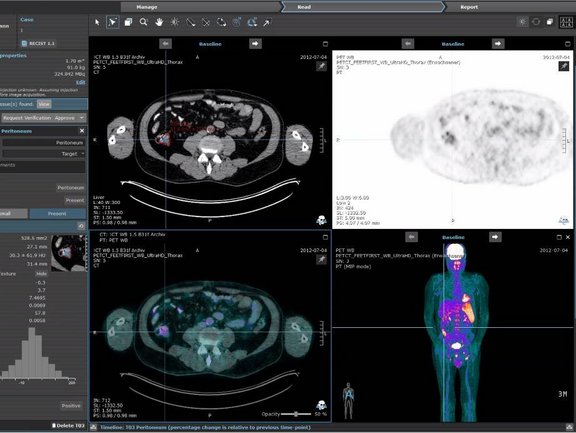
With mint Lesion 3.4, reproducible assessment and structured reporting of significant image observations are easier than ever.
Numerous improvements and new functionalities related to the image data handling and display streamline the image assessment. As such, for instance, a refined image series browser provides instantaneous access to image combined with a single-click customizability of an image hanging. Next to the existing cross reference lines, a new cross-hair tool allows for easy spatial navigation, which includes the picking of lesions in a rotating 3D MIP view of PET image data.
An area of constant refinements and enhancements is also the support for specific reading profiles targeting specific read tasks in Radiology. Usually, the referrals require certain critical aspects to be addressed in a clear and reproducible manner as they correlate with tipping points for further decisions with regards to diagnosis and treatment. Mint Lesion implements the read tasks and related international guidelines and criteria in detail and assures the adherence and consistency of radiological reports. In mint Lesion 3.4, head and neck tumor entities have been added and all reading profiles with TNM criteria involvement have been updated to the latest version of TNM. Furthermore, new reading profiles have been added. As one example for this, a dedicated reading profile to assess the indication of a surgical treatment of pancreatic cancer facilitates the reproducible reporting of complex vascular involvements with the help of automatically generated, illustrative 3D drawings in a structured report.