The recent 3.8 release brings with it a multitude of new features and refinements that further facilitate reporting, interdisciplinary collaboration, and patient management in clinical routine and clinical trials. Users worldwide can now benefit from multiple general innovations within the software platform as well as specific updates concerning radiomics, various reading templates, and evaluation criteria, e.g. PI-RADS or TNM 8.0.
mint Lesion™ enables its users to see the big picture, to leave no data behind on the image with its one of a kind read process which directly links any findings to the imaging data. New changes in the user interface, such as directly available information in the read screen on historic values of all measurements and user-defined answers via tables and charts, provide the user with all information necessary for a holistic read process. To advance this process, a revision of the anatomical location selection dialog improves the readability of long location names, which in turn facilitates the differentiation of major locations from sub-locations.
Since we understand radiomics to be the driving force behind the advancement of personalized therapy, further improvements were made in this area: radiomics features can now also be calculated on PET and ADC image measurements, enabling the user to gain valuable information that allows them to potentially decide on the best therapy approach upon the first imaging. Through a new dialog, multiple radiomics exports with differing configurations can be conveniently triggered and used to analyze tumor heterogeneity right from the start. mint Lesion™ supports its users in their radiomics research by collecting radiomics data in the background of their day-to-day reading activity, and these new adaptations, among others, will further empower the collection of valuable data in clinical trials as well as in clinical routine.
Additional changes within mint Lesion™ 3.8 include the ability to draw prostate lesions by free-hand contour in the PI-RADS prostate sector map without being limited to ellipse shapes, leading to a more precise indication of the tumor shape itself. Moreover, the head and neck carcinoma staging criteria TNM 8.0 has been added along with rules to calculate the TNM staging categories automatically based on image findings and answers provided in the reading templates – as mint Lesion™ users are accustomed to.
In ongoing clinical trials, it is essential to remain flexible. For this reason, it is now also possible by configuration to add an additional trial arm to an already existing trial. The new trial arm will be available for all patients associated with the trial. From now on, users are also able to determine whether patients should be automatically added to a trial based on certain DICOM attribute values.
For an overview of all new features and enhancements of the 3.8 release, feel free to contact us.
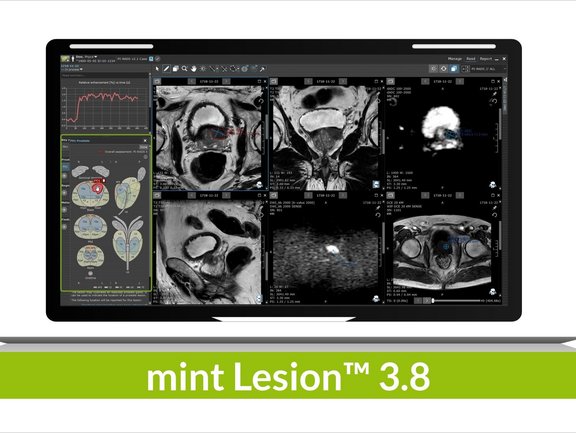
mint Lesion™ 3.8. Release: What’s New?
Related Resources
Related Resources
Comparison of iRECIST and RECIST 1.1 for Evaluating Immunotherapy in Melanoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
In a retrospective study conducted at the University Hospital Cologne, the radiological criteria iRECIST and RECIST 1.1 were compared for assessing…

University Hospital Cologne: Comparison of iRECIST and RECIST 1.1 for Evaluating Immunotherapy in Melanoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
A retrospective study conducted at University Hospital Cologne compared two criteria for assessing therapeutic response to immunotherapy: iRECIST and…

Developing Standardized Reporting Templates for Sarcomas: Insights from Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Kunz
Sarcomas are a rare and heterogeneous group of malignant tumors that pose significant challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. Within the framework…