Traditionally medical image analysis has been done through visual interpretation of static images. In the past decade, with the advent of sophisticated measurement tools, it has become possible to convert simple digital images into data mines which contain first, second and higher-order statistics. When administered and utilized by an expert reader, with the right tool, they have proven to have potential for increased diagnostic and potential prognostic accuracy.
At Mint Medical, for over a decade, we have been developing structured-data platform and algorithms that routinely capture higher-order texture analysis in personalized clinical workflows that adhere to national and societies’ guidelines. Currently mint Lesion features over twenty-five different radiological workflow protocols that are configured to record texture data in a routine clinical setting.
Some of the recent academic results driven by mint Lesion were published in 2017 at the University of Ulm in which authors concluded that MRI texture analysis may assist in differentiating low-grade chondrosarcoma from enchondroma [1]. Utilizing radiomics features measurement to provide insight into tumor characterization as a non-invasive biomarker is quite revolutionary: We can potentially see transformative effects on improving the accuracy of biopsy results.
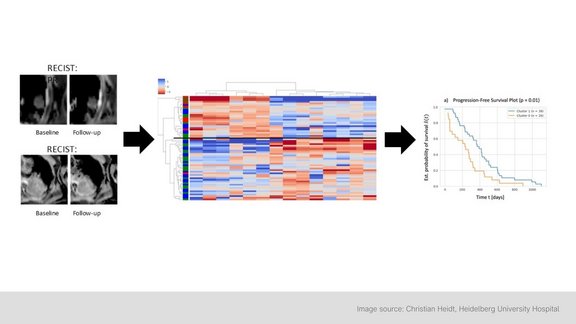
Another study at the University of Cologne using mint Lesion’s workflows and radiomics tools concluded that there may be potential for MRI-based texture analysis in the arterial and venous phase for the early prediction of progressive disease after trans-arterial radioembolization (TARE) [2]. We fervently continue to support the academic community globally in its pursuit of advancing towards precision medicine in which imaging biomarkers have potential to help predict the right treatment and affect active surveillance of patient population.
“With mint Lesion, our vision for imaging is to transform patient therapy by bridging the gap between traditional and individualized care through utilization of the only truth, that is the intelligently structured imaging and clinical data. We strive to leave 0% chance to misinterpretation when it comes to patient lives,” says Mint Medical’s CEO Dr. Matthias Baumhauer.
As we constantly thrive to push the envelope of Intelligent computing, at Mint Medical, we have actively partnered and complied with Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance [3] profiles and have successfully validated against the Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative, including the first, second-order texture analysis [4].
[1] https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-016-2952-5
[2] https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2004-2
[3] https://www.rsna.org/en/research/quantitative-imaging-biomarkers-alliance