More automation within mint Lesion™? Automated context-dependent template selection, filtering of relevant questions or even fully automated organ and lesion volume segmentation? Those features are all closer than ever.
Last March, Mint Medical was acquired by Brainlab, a leader in image-guided surgery and radiotherapy. Brainlab planning and intra-operative applications have long been powered by its Anatomic Patient Model – a multi-modal, biomechanical, AI- and Atlas-based simulation of an individual patient’s anatomy.
We now have connected the Anatomic Patient Model (APM) to mint Lesion™. The APM was made available through the Brainlab subsidy Snke OS, which set out to build an open health-tech platform around the Brainlab core technology frameworks.
One of our first prototypic use cases is image/structure-aware filtering of questions/templates: By clicking on an anatomic structure inside the viewer, mint Lesion™ automatically detects the structure within the slice set and suggests the relevant questions. Another use case is the automated detection and full segmentation of cranial lesions, for effortless volumetric tumor monitoring applications. However, this is just a teaser of the functionalities that will be bound to come.
If you are curious and would like to try our first steps to automate mint Lesion™ with the Anatomic Patient Model, discuss the use cases you would like to see, or even want to leverage the APM in your own software application, visit us at one of our booths at the RSNA.
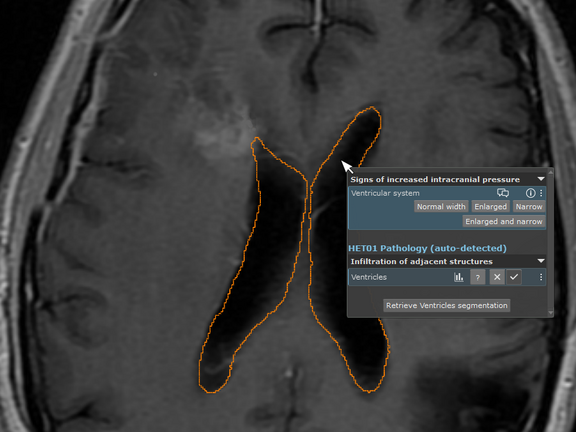
„Anatomical GPS“ for mint Lesion™: Leveraging the Snke OS/Brainlab Anatomic Patient Model to drive anatomic-context-awareness and automation within mint Lesion™
Related Resources
Related Resources

Leave No Data Behind: Commitment to Data Excellence
At Mint Medical, we understand data as a cornerstone for improving patient care and groundbreaking research. Our mission is clear: Leave No Data…

ESOI-EORTC Workshop: Hands-On Training in Assessing Tumor Response to Treatment
The ESOI-EORTC workshop, hosted by the European Society of Oncological Imaging (ESOI) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of…

Project RACOON-RESCUE: Advancing Diagnosis and Treatment for Pediatric Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Pediatric Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL), a type of lymph node cancer, is the fourth most common tumor in children and adolescents. Radiological…