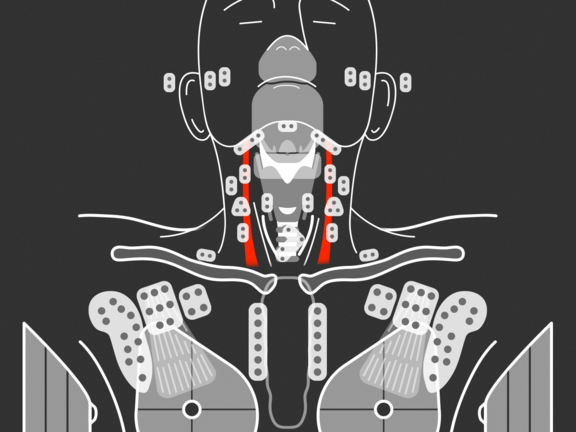
With the aid of various clinical reading templates, mint Lesion provides context-specific support in the application of established radiological criteria and guidelines for a more efficient investigation and documentation of radiological findings. mint Lesion employs a structured approach to interpreting relevant findings in medical images so as to highlight specific aspects of a tumor disease that influence patient treatment.
- TNM Staging (8th Edition)
- Pharynx/Larynx cancer
- Lung cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Liver cancer
- ACR RADS
- PI-RADS v2
- NI-RADS
- BI-RADS
- Lung-RADS
- LI-RADS
The TNM Classification of the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) is a worldwide established system for the assessment of malignant tumors. Categorizing tumor diseases in clinically homogenous groups according to the anatomic extent of disease through the process of staging provides salient information for individual therapy decision-making and prognostic prediction. Furthermore, this system provides a basis for the evaluation of promising therapies in oncological research, especially in communication and information exchange between cancer treatment centers.
A further initiative by the American College of Radiology (ACR), the Reporting and Data Systems (RADS), comprises a group of reading criteria for quality assurance in radiology. A standardized terminology and defined classification algorithms enhance the imaging reading process as well as the subsequent assessment of the information gathered.