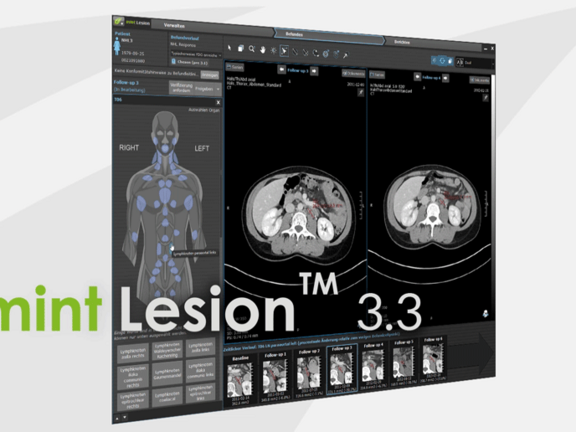
Mint Medical is pleased to announce the recent release of their software product version 3.3 of mint LesionTM which was completed during recent weeks. Mint Medical CEO, Dr. Matthias Baumhauer provides his insight as to what can be expected in this highly anticipated version of mint LesionTM .
What is new in mint Lesion 3.3?
An additional benefit of mint Lesion 3.3 is a new system architecture for the recording of structured data and modellings of operational procedures. For the applicants, this means the complement of new report profiles without extensive programming and existing reports which can easily be corrected and kept up-to-date. In the course of adding these innovations, additional new guidelines and reporting templates have also been added including mesothelioma, lymphoma and immune-therapy criteria. These extensive innovations include multiple new features and improvements such as the processing of 4D data including DCE-MRI, the implementation of the RadLex-nomenclature and the development of our interface for the connection of mint LesionTM to KIS and RIS systems as well as electronic patient files.
Which development processes are directly related to this release?
With the technical standards implemented in mint Lesion 3.3, we are prospectively able to provide and adapt specific support for diagnosing and reporting different indications faster and more flexibly than ever before. At a recent Radiology convention (RONTGEN Congress May 2017 Leipzig, Germany) in Leipzig several new dedicated profiles were presented relevant to the following guidelines:
- Guidelines provided by the American College of Radiology, such as ACR ® LI-RADS, Lung-RADS and BI-RADS
- Fleischner-criteria for the documentation and patient management of random reports of the lung
- Guidelines of the DRG initiative for structured diagnosing, such as Rectum-CA, Colon-CA and Pancreas-CA
- The Ann Arbor staging for lymphoma
- Pediatric oncological evaluations such as neuroblastoma and hepatoblastoma
Furthermore, we continue to increase the ease of use for performing these evaluations with every product version. As an example, a new procedure currently developed allows for the automatic retrieval of observations among longitudinal patient studies. For measuring lesions, there are also exciting new developments forthcoming in mint Lesion. Perhaps one of the most exciting is a process which will enable the determination of heterogenic lesions, which are tumors with necrotic parts, as whole volumes and subdivided volumes. Mint will also soon make it possible to show changes in a lesion´s appearance through histograms and texture analyses.
Which market trends and developments underline the importance of assisted structured analysis?
New imaging processes, such as molecular imaging are becoming increasingly more common in the clinical routine. In the scope of oncologic radiology for example, the need for the analysis of imaging data by multiple criteria and algorithims has become much more common. Communication with referring physicians as well as collaboration among radiologist has set new challenges. Comprehensive and guideline-conforming analysis with a structured reporting form contribute in particular to an unambiguous and efficient transfer of information.