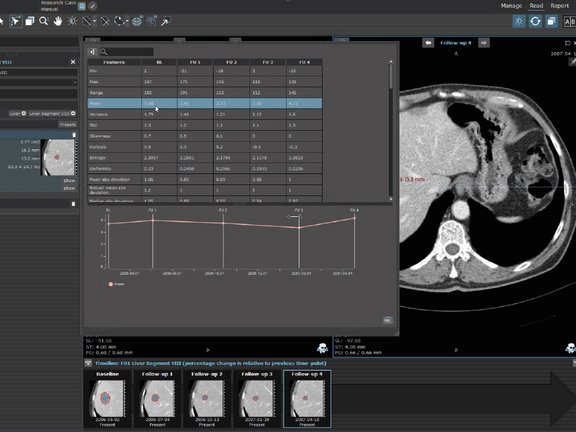
The benefits that texture analysis and radiomics have shown already, and the improved availability of large data sets led to an increased interest in the extraction of quantitative features from medical images. Through quantification, images are converted into mineable data that, subsequently analyzed, improve diagnostic accuracy and prognosis assessment and enhance predictive power for decision support.
Although radiomics offers high potential for boosting precision medicine, its implementation in a clinical setting harbors substantial challenges - which mint Lesion successfully addresses:
Reproducibility
Numerous studies have shown substantial variability in radiomics features that originated in differences in image acquisition parameters, reconstruction algorithms, and calculation parameters. Due to the growing demand for harmonization among radiomics research, the imaging biomarker standardization initiative (IBSI)1 established standard recommendations for radiomics feature nomenclature and image processing protocols required before extraction. mint Lesion validated its radiomics features against the benchmark data set by the ISBI.
Prospective collection of quantitative data and data curation
In current general practice, radiologic images are often evaluated qualitatively, and the written (mostly prose) reports do not use any standard lexicon, creating massive image repositories that are underused and inaccessible for data curation. With mint Lesion, data from routine radiologic evaluations is converted into quantitative feature data and combined with knowledge bases and longitudinal information, making high-quality data capture, collection, and curation a reality.
Data sharing
One of the biggest challenges of using radiomics-based models for decision support is the sharing of image metadata between systems and across multiple sites to create data sets of relevant size. The radiomics features in mint Lesion can be exported to XML or CSV. Besides, the images from mint Lesion support several data representations common in industry and research, like for example NRRD / NIFTI, DICOM RT Struct, or DICOM Segmentation Objects.
In a short video, we show a radiomics research case with longitudinally connected data and graphs for extracted 1st and 2nd order parameters. The video also shows our radiomics display widget that can be used to change the configuration on the fly, as well as the export of the features on a single patient or patient cohort level.
1
arxiv.org/abs/1612.07003 Zwanenburg, A., Leger, S., Vallières, M., Löck, S., & et al. (2016). Image biomarker standardization initiative. ArXiv, arXiv:1612.07003v6.